Configuration
Format
A configuration file is a free-form ASCII text file with a structure that is similar to that of a Makefile, with the default nameDoxyfile. It is parsed by doxygen. The file may contain tabs and newlines for formatting purposes. The statements in the file are case-sensitive. Comments may be placed anywhere within the file (except within quotes). Comments begin with the # character and end at the end of the line.
The file essentially consists of a list of assignment statements. Each statement consists of a TAG_NAME written in capitals, followed by the = character and one or more values. If the same tag is assigned more than once, the last assignment overwrites any earlier assignment. For options that take a list as their argument, the += operator can be used instead of = to append new values to the list. Values are sequences of non-blanks. If the value should contain one or more blanks it must be surrounded by quotes ("..."). Multiple lines can be concatenated by inserting a backslash (\) as the last character of a line. Environment variables can be expanded using the pattern $(ENV_VARIABLE_NAME).
You can also include part of a configuration file from another configuration file using a @INCLUDE tag as follows:
@INCLUDE = config_file_name
@INCLUDE_PATH tag with these paths before the @INCLUDE tag, e.g: @INCLUDE_PATH = my_config_dir
The configuration options can be divided into several categories. Below is an alphabetical index of the tags that are recognized followed by the descriptions of the tags grouped by category.
Project related options
DOXYFILE_ENCODING- This tag specifies the encoding used for all characters in the config file that follow. The default is UTF-8 which is also the encoding used for all text before the first occurrence of this tag. Doxygen uses libiconv (or the iconv built into libc) for the transcoding. See http://www.gnu.org/software/libiconv for the list of possible encodings.
PROJECT_NAME- The
PROJECT_NAMEtag is a single word (or a sequence of words surrounded by double-quotes) that should identify the project for which the documentation is generated. This name is used in the title of most generated pages and in a few other places. PROJECT_NUMBER- The
PROJECT_NUMBERtag can be used to enter a project or revision number. This could be handy for archiving the generated documentation or if some version control system is used. OUTPUT_DIRECTORY- The
OUTPUT_DIRECTORYtag is used to specify the (relative or absolute) path into which the generated documentation will be written. If a relative path is entered, it will be relative to the location where doxygen was started. If left blank the current directory will be used. CREATE_SUBDIRS- If the
CREATE_SUBDIRStag is set toYES, then doxygen will create 4096 sub-directories (in 2 levels) under the output directory of each output format and will distribute the generated files over these directories. Enabling this option can be useful when feeding doxygen a huge amount of source files, where putting all generated files in the same directory would otherwise causes performance problems for the file system. OUTPUT_LANGUAGE- The
OUTPUT_LANGUAGEtag is used to specify the language in which all documentation generated by doxygen is written. Doxygen will use this information to generate all constant output in the proper language. The default language is English, other supported languages are: Afrikaans, Arabic, Brazilian, Catalan, Chinese, Croatian, Czech, Danish, Dutch, Finnish, French, German, Greek, Hungarian, Italian, Japanese, Korean, Lithuanian, Norwegian, Persian, Polish, Portuguese, Romanian, Russian, Serbian, Slovak, Slovene, Spanish, Swedish, and Ukrainian. USE_WINDOWS_ENCODING- This tag can be used to specify the encoding used in the generated output. The encoding is not always determined by the language that is chosen, but also whether or not the output is meant for Windows or non-Windows users. In case there is a difference, setting the
USE_WINDOWS_ENCODINGtag toYESforces the Windows encoding, (this is the default for the Windows binary), whereas setting the tag toNOuses a Unix-style encoding (the default for all platforms other than Windows). BRIEF_MEMBER_DESC- If the
BRIEF_MEMBER_DESCtag is set toYES(the default) doxygen will include brief member descriptions after the members that are listed in the file and class documentation (similar to JavaDoc). Set to NO to disable this. REPEAT_BRIEF- If the
REPEAT_BRIEFtag is set toYES(the default) doxygen will prepend the brief description of a member or function before the detailed description- Note:
- If both
HIDE_UNDOC_MEMBERSandBRIEF_MEMBER_DESCare set toNO, the brief descriptions will be completely suppressed.
ABBREVIATE_BRIEF- This tag implements a quasi-intelligent brief description abbreviator that is used to form the text in various listings. Each string in this list, if found as the leading text of the brief description, will be stripped from the text and the result after processing the whole list, is used as the annotated text. Otherwise, the brief description is used as-is. If left blank, the following values are used ("\$name" is automatically replaced with the name of the entity): "The $name class" "The $name widget" "The $name file" "is" "provides" "specifies" "contains" "represents" "a" "an" "the".
ALWAYS_DETAILED_SEC- If the
ALWAYS_DETAILED_SECandREPEAT_BRIEFtags are both set toYESthen doxygen will generate a detailed section even if there is only a brief description. INLINE_INHERITED_MEMB- If the
INLINE_INHERITED_MEMBtag is set toYES, doxygen will show all inherited members of a class in the documentation of that class as if those members were ordinary class members. Constructors, destructors and assignment operators of the base classes will not be shown. FULL_PATH_NAMES- If the
FULL_PATH_NAMEStag is set toYESdoxygen will prepend the full path before files name in the file list and in the header files. If set to NO the shortest path that makes the file name unique will be used STRIP_FROM_PATH- If the
FULL_PATH_NAMEStag is set toYESthen theSTRIP_FROM_PATHtag can be used to strip a user-defined part of the path. Stripping is only done if one of the specified strings matches the left-hand part of the path. The tag can be used to show relative paths in the file list. If left blank the directory from which doxygen is run is used as the path to strip. STRIP_FROM_INC_PATH- The
STRIP_FROM_INC_PATHtag can be used to strip a user-defined part of the path mentioned in the documentation of a class, which tells the reader which header file to include in order to use a class. If left blank only the name of the header file containing the class definition is used. Otherwise one should specify the include paths that are normally passed to the compiler using the -I flag. CASE_SENSE_NAMES- If the
CASE_SENSE_NAMEStag is set toNOthen doxygen will only generate file names in lower-case letters. If set toYESupper-case letters are also allowed. This is useful if you have classes or files whose names only differ in case and if your file system supports case sensitive file names. Windows users are advised to set this option to NO. SHORT_NAMES- If the
SHORT_NAMEStag is set toYES, doxygen will generate much shorter (but less readable) file names. This can be useful is your file systems doesn't support long names like on DOS, Mac, or CD-ROM. JAVADOC_AUTOBRIEF- If the
JAVADOC_AUTOBRIEFis set toYESthen doxygen will interpret the first line (until the first dot) of a JavaDoc-style comment as the brief description. If set to NO (the default), the Javadoc-style will behave just like regular Qt-style comments (thus requiring an explicit @brief command for a brief description.) QT_AUTOBRIEF- If the
QT_AUTOBRIEFis set toYESthen doxygen will interpret the first line (until the first dot) of a Qt-style comment as the brief description. If set to NO (the default), the Qt-style will behave just like regular Qt-style comments (thus requiring an explicit \brief command for a brief description.) BUILTIN_STL_SUPPORT- If you use STL classes (i.e. std::string, std::vector, etc.) but do not want to include (a tag file for) the STL sources as input, then you should set this tag to
YESin order to let doxygen match functions declarations and definitions whose arguments contain STL classes (e.g. func(std::string); v.s. func(std::string) {}). This also make the inheritance and collaboration diagrams that involve STL classes more complete and accurate. CPP_CLI_SUPPORT- If you use Microsoft's C++/CLI language, you should set this option to YES to enable parsing support.
SIP_SUPPORT- Set the SIP_SUPPORT tag to YES if your project consists of sip sources only. Doxygen will parse them like normal C++ but will assume all classes use public instead of private inheritance when no explicit protection keyword is present.
IDL_PROPERTY_SUPPORT- For Microsoft's IDL there are propget and propput attributes to indicate getter and setter methods for a property. Setting this option to
YES(the default) will make doxygen to replace the get and set methods by a property in the documentation. This will only work if the methods are indeed getting or setting a simple type. If this is not the case, or you want to show the methods anyway, you should set this option toNO. DISTRIBUTE_GROUP_DOC- If member grouping is used in the documentation and the DISTRIBUTE_GROUP_DOC tag is set to YES, then doxygen will reuse the documentation of the first member in the group (if any) for the other members of the group. By default all members of a group must be documented explicitly.
MULTILINE_CPP_IS_BRIEF- The MULTILINE_CPP_IS_BRIEF tag can be set to YES to make Doxygen treat a multi-line C++ special comment block (i.e. a block of //! or /// comments) as a brief description. This used to be the default behaviour. The new default is to treat a multi-line C++ comment block as a detailed description. Set this tag to YES if you prefer the old behaviour instead. Note that setting this tag to YES also means that rational rose comments are not recognized any more.
INHERIT_DOCS- If the
INHERIT_DOCStag is set toYES(the default) then an undocumented member inherits the documentation from any documented member that it re-implements. SEPARATE_MEMBER_PAGES- If the
SEPARATE_MEMBER_PAGEStag is set toYES, then doxygen will produce a new page for each member. If set toNO, the documentation of a member will be part of the file/class/namespace that contains it. TAB_SIZE- the
TAB_SIZEtag can be used to set the number of spaces in a tab. Doxygen uses this value to replace tabs by spaces in code fragments. ALIASES- This tag can be used to specify a number of aliases that acts as commands in the documentation. An alias has the form For example adding
name=value
will allow you to put the command \sideeffect (or @sideeffect) in the documentation, which will result in a user-defined paragraph with heading "Side Effects:". You can put \n's in the value part of an alias to insert newlines."sideeffect=\par Side Effects:\n"
OPTIMIZE_OUTPUT_FOR_C- Set the
OPTIMIZE_OUTPUT_FOR_Ctag toYESif your project consists of C sources only. Doxygen will then generate output that is more tailored for C. For instance, some of the names that are used will be different. The list of all members will be omitted, etc. OPTIMIZE_OUTPUT_JAVA- Set the OPTIMIZE_OUTPUT_JAVA tag to YES if your project consists of Java or Python sources only. Doxygen will then generate output that is more tailored for that language. For instance, namespaces will be presented as packages, qualified scopes will look different, etc.
OPTIMIZE_FOR_FORTRAN- Set the
OPTIMIZE_FOR_FORTRANtag toYESif your project consists of Fortran sources. Doxygen will then generate output that is tailored for Fortran. OPTIMIZE_OUTPUT_VHDL- Set the
OPTIMIZE_OUTPUT_VHDLtag toYESif your project consists of VHDL sources. Doxygen will then generate output that is tailored for VHDL. SUBGROUPING- Set the
SUBGROUPINGtag toYES(the default) to allow class member groups of the same type (for instance a group of public functions) to be put as a subgroup of that type (e.g. under the Public Functions section). Set it toNOto prevent subgrouping. Alternatively, this can be done per class using the \nosubgrouping command. TYPEDEF_HIDES_STRUCT- When
TYPEDEF_HIDES_STRUCTis enabled, a typedef of a struct, union, or enum is documented as struct, union, or enum with the name of the typedef. Sotypedef struct TypeS {} TypeT, will appear in the documentation as a struct with nameTypeT. When disabled the typedef will appear as a member of a file, namespace, or class. And the struct will be namedTypeS. This can typically be useful for C code in case the coding convention dictates that all compound types are typedef'ed and only the typedef is referenced, never the tag name. SYMBOL_CACHE_SIZE- The
SYMBOL_CACHE_SIZEdetermines the size of the internal cache use to determine which symbols to keep in memory and which to flush to disk. When the cache is full, less often used symbols will be written to disk. For small to medium size projects (<1000 input files) the default value is probably good enough. For larger projects a too small cache size can cause doxygen to be busy swapping symbols to and from disk most of the time causing a significant performance penality. If the system has enough physical memory increasing the cache will improve the performance by keeping more symbols in memory. Note that the value works on a logarithmic scale so increasing the size by one will rougly double the memory usage. The cache size is given by this formula: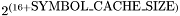 . The valid range is 0..9, the default is 0, corresponding to a cache size of
. The valid range is 0..9, the default is 0, corresponding to a cache size of 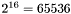 symbols.
symbols.
Build related options
EXTRACT_ALL- If the
EXTRACT_ALLtag is set toYESdoxygen will assume all entities in documentation are documented, even if no documentation was available. Private class members and static file members will be hidden unless theEXTRACT_PRIVATEandEXTRACT_STATICtags are set toYES- Note:
- This will also disable the warnings about undocumented members that are normally produced when
WARNINGSis set toYES
EXTRACT_PRIVATE- If the
EXTRACT_PRIVATEtag is set toYESall private members of a class will be included in the documentation. EXTRACT_STATIC- If the
EXTRACT_STATICtag is set toYESall static members of a file will be included in the documentation. EXTRACT_LOCAL_CLASSES- If the
EXTRACT_LOCAL_CLASSEStag is set toYESclasses (and structs) defined locally in source files will be included in the documentation. If set to NO only classes defined in header files are included. Does not have any effect for Java sources. EXTRACT_ANON_NSPACES- If this flag is set to YES, the members of anonymous namespaces will be extracted and appear in the documentation as a namespace called 'anonymous_namespace{file}', where file will be replaced with the base name of the file that contains the anonymous namespace. By default anonymous namespace are hidden.
EXTRACT_LOCAL_METHODS- This flag is only useful for Objective-C code. When set to
YESlocal methods, which are defined in the implementation section but not in the interface are included in the documentation. If set toNO(the default) only methods in the interface are included. HIDE_UNDOC_MEMBERS- If the
HIDE_UNDOC_MEMBERStag is set toYES, doxygen will hide all undocumented members inside documented classes or files. If set toNO(the default) these members will be included in the various overviews, but no documentation section is generated. This option has no effect ifEXTRACT_ALLis enabled. HIDE_UNDOC_CLASSES- If the
HIDE_UNDOC_CLASSESStag is set toYES, doxygen will hide all undocumented classes. If set toNO(the default) these classes will be included in the various overviews. This option has no effect ifEXTRACT_ALLis enabled. HIDE_FRIEND_COMPOUNDS- If the
HIDE_FRIEND_COMPOUNDStag is set toYES, Doxygen will hide all friend (class|struct|union) declarations. If set toNO(the default) these declarations will be included in the documentation. HIDE_IN_BODY_DOCS- If the
HIDE_IN_BODY_DOCStag is set toYES, Doxygen will hide any documentation blocks found inside the body of a function. If set toNO(the default) these blocks will be appended to the function's detailed documentation block. INTERNAL_DOCS- The
INTERNAL_DOCStag determines if documentation that is typed after a \internal command is included. If the tag is set toNO(the default) then the documentation will be excluded. Set it toYESto include the internal documentation. HIDE_SCOPE_NAMES- If the
HIDE_SCOPE_NAMEStag is set toNO(the default) then doxygen will show members with their full class and namespace scopes in the documentation. If set toYESthe scope will be hidden. SHOW_INCLUDE_FILES- If the SHOW_INCLUDE_FILES tag is set to YES (the default) then doxygen will put a list of the files that are included by a file in the documentation of that file.
INLINE_INFO- If the
INLINE_INFOtag is set toYES(the default) then a tag [inline] is inserted in the documentation for inline members. SORT_MEMBER_DOCS- If the
SORT_MEMBER_DOCStag is set toYES(the default) then doxygen will sort the (detailed) documentation of file and class members alphabetically by member name. If set toNOthe members will appear in declaration order. SORT_BRIEF_DOCS- If the
SORT_BRIEF_DOCStag is set toYESthen doxygen will sort the brief descriptions of file, namespace and class members alphabetically by member name. If set toNO(the default) the members will appear in declaration order. SORT_GROUP_NAMES- If the
SORT_GROUP_NAMEStag is set toYESthen doxygen will sort the hierarchy of group names into alphabetical order. If set toNO(the default) the group names will appear in their defined order. SORT_BY_SCOPE_NAME- If the
SORT_BY_SCOPE_NAMEtag is set toYES, the class list will be sorted by fully-qualified names, including namespaces. If set to NO (the default), the class list will be sorted only by class name, not including the namespace part.- Note:
- This option is not very useful if
HIDE_SCOPE_NAMESis set toYES.This option applies only to the class list, not to the alphabetical list.
GENERATE_DEPRECATEDLIST- The GENERATE_DEPRECATEDLIST tag can be used to enable (YES) or disable (NO) the deprecated list. This list is created by putting \deprecated commands in the documentation.
GENERATE_TODOLIST- The GENERATE_TODOLIST tag can be used to enable (YES) or disable (NO) the todo list. This list is created by putting \todo commands in the documentation.
GENERATE_TESTLIST- The GENERATE_TESTLIST tag can be used to enable (YES) or disable (NO) the test list. This list is created by putting \test commands in the documentation.
GENERATE_BUGLIST- The GENERATE_BUGLIST tag can be used to enable (YES) or disable (NO) the bug list. This list is created by putting \bug commands in the documentation.
ENABLED_SECTIONS- The
ENABLED_SECTIONStag can be used to enable conditional documentation sections, marked by \if <section-label> ... \endif and \cond <section-label> ... \endcond blocks. MAX_INITIALIZER_LINES- The
MAX_INITIALIZER_LINEStag determines the maximum number of lines that the initial value of a variable or define can be. If the initializer consists of more lines than specified here it will be hidden. Use a value of 0 to hide initializers completely. The appearance of the value of individual variables and defines can be controlled using \showinitializer or \hideinitializer command in the documentation. SHOW_USED_FILES- Set the
SHOW_USED_FILEStag toNOto disable the list of files generated at the bottom of the documentation of classes and structs. If set toYESthe list will mention the files that were used to generate the documentation. SHOW_DIRECTORIES- If the sources in your project are distributed over multiple directories then setting the SHOW_DIRECTORIES tag to YES will show the directory hierarchy in the documentation.
SHOW_FILES- Set the
SHOW_FILEStag toNOto disable the generation of the Files page. This will remove the Files entry from the Quick Index and from the Folder Tree View (if specified). The default isYES. SHOW_NAMESPACES- Set the
SHOW_NAMESPACEStag toNOto disable the generation of the Namespaces page. This will remove the Namespaces entry from the Quick Index and from the Folder Tree View (if specified). The default isYES.
Options related to warning and progress messages
QUIET- The
QUIETtag can be used to turn on/off the messages that are generated to standard output by doxygen. Possible values areYESandNO, whereYESimplies that the messages are off. If left blankNOis used. WARNINGS- The
WARNINGStag can be used to turn on/off the warning messages that are generated to standard error by doxygen. Possible values areYESandNO, whereYESimplies that the warnings are on. If left blankNOis used.Tip: Turn warnings on while writing the documentation.
WARN_IF_UNDOCUMENTED- If
WARN_IF_UNDOCUMENTEDis set toYES, then doxygen will generate warnings for undocumented members. IfEXTRACT_ALLis set toYESthen this flag will automatically be disabled. WARN_IF_DOC_ERROR- If
WARN_IF_DOC_ERRORis set toYES, doxygen will generate warnings for potential errors in the documentation, such as not documenting some parameters in a documented function, or documenting parameters that don't exist or using markup commands wrongly. WARN_NO_PARAMDOC- This
WARN_NO_PARAMDOCoption can be abled to get warnings for functions that are documented, but have no documentation for their parameters or return value. If set toNO(the default) doxygen will only warn about wrong or incomplete parameter documentation, but not about the absence of documentation. WARN_FORMAT- The
WARN_FORMATtag determines the format of the warning messages that doxygen can produce. The string should contain the$file,$line, and$texttags, which will be replaced by the file and line number from which the warning originated and the warning text. WARN_LOGFILE- The
WARN_LOGFILEtag can be used to specify a file to which warning and error messages should be written. If left blank the output is written to stderr.
Input related options
INPUT- The
INPUTtag is used to specify the files and/or directories that contain documented source files. You may enter file names likemyfile.cppor directories like/usr/src/myproject. Separate the files or directories with spaces.
Note: If this tag is empty the current directory is searched.
INPUT_ENCODING- This tag can be used to specify the character encoding of the source files that doxygen parses. Internally doxygen uses the UTF-8 encoding, which is also the default input encoding. Doxygen uses libiconv (or the iconv built into libc) for the transcoding. See the libiconv documentation for the list of possible encodings.
FILE_PATTERNS- If the value of the
INPUTtag contains directories, you can use theFILE_PATTERNStag to specify one or more wildcard patterns (like*.cpp and*.h ) to filter out the source-files in the directories. If left blank the following patterns are tested:.c *.cc *.cxx *.cpp *.c++ *.java *.ii *.ixx *.ipp *.i++ *.inl *.h *.hh *.hxx *.hpp .h++ *.idl *.odl *.cs *.php *.php3 *.inc *.m *.mm FILE_VERSION_FILTER- The
FILE_VERSION_FILTERtag can be used to specify a program or script that doxygen should invoke to get the current version for each file (typically from the version control system). Doxygen will invoke the program by executing (via popen()) the commandcommand input-file, wherecommandis the value of theFILE_VERSION_FILTERtag, andinput-fileis the name of an input file provided by doxygen. Whatever the program writes to standard output is used as the file version.Example of using a shell script as a filter for Unix:
FILE_VERSION_FILTER = "/bin/sh versionfilter.sh"
Example shell script for CVS:
#!/bin/sh cvs status $1 | sed -n 's/^[ \]*Working revision:[ \t]*\([0-9][0-9\.]*\).*/\1/p'
Example shell script for Subversion:
#!/bin/sh svn stat -v $1 | sed -n 's/^[ A-Z?\*|!]\{1,15\}/r/;s/ \{1,15\}/\/r/;s/ .*//p'Example filter for ClearCase:
FILE_VERSION_INFO = "cleartool desc -fmt \%Vn"
LAYOUT_FILE- The
LAYOUT_FILEtag can be used to specify a layout file which will be parsed by doxygen. The layout file controls the global structure of the generated output files in an output format independent way. The create the layout file that represents doxygen's defaults, run doxygen with the -l option. You can optionally specify a file name after the option, if omitted DoxygenLayout.xml will be used as the name of the layout file. Note that if you run doxygen from a directory containing a file called DoxygenLayout.xml, doxygen will parse it automatically even if theLAYOUT_FILEtag is left empty. RECURSIVE- The
RECURSIVEtag can be used to specify whether or not subdirectories should be searched for input files as well. Possible values areYESandNO. If left blankNOis used. EXCLUDE- The
EXCLUDEtag can be used to specify files and/or directories that should excluded from theINPUTsource files. This way you can easily exclude a subdirectory from a directory tree whose root is specified with theINPUTtag. EXCLUDE_SYMLINKS- The
EXCLUDE_SYMLINKStag can be used select whether or not files or directories that are symbolic links (a Unix filesystem feature) are excluded from the input. EXCLUDE_PATTERNS- If the value of the
INPUTtag contains directories, you can use theEXCLUDE_PATTERNStag to specify one or more wildcard patterns to exclude certain files from those directories.Note that the wildcards are matched against the file with absolute path, so to exclude all test directories use the pattern
*/test/* EXAMPLE_PATH- The
EXAMPLE_PATHtag can be used to specify one or more files or directories that contain example code fragments that are included (see the \include command in section \include). EXAMPLE_RECURSIVE- If the
EXAMPLE_RECURSIVEtag is set toYESthen subdirectories will be searched for input files to be used with the \include or \dontinclude commands irrespective of the value of theRECURSIVEtag. Possible values areYESandNO. If left blankNOis used. EXAMPLE_PATTERNS- If the value of the
EXAMPLE_PATHtag contains directories, you can use theEXAMPLE_PATTERNStag to specify one or more wildcard pattern (like *.cpp and *.h) to filter out the source-files in the directories. If left blank all files are included. IMAGE_PATH- The
IMAGE_PATHtag can be used to specify one or more files or directories that contain images that are to be included in the documentation (see the \image command). INPUT_FILTER- The
INPUT_FILTERtag can be used to specify a program that doxygen should invoke to filter for each input file. Doxygen will invoke the filter program by executing (via popen()) the command:<filter> <input-file>
where <filter> is the value of the
INPUT_FILTERtag, and <input-file> is the name of an input file. Doxygen will then use the output that the filter program writes to standard output. FILTER_PATTERNS- The
FILTER_PATTERNStag can be used to specify filters on a per file pattern basis. Doxygen will compare the file name with each pattern and apply the filter if there is a match. The filters are a list of the form: pattern=filter (like*.cpp=my_cpp_filter). SeeINPUT_FILTERfor further info on how filters are used. IfFILTER_PATTERNSis empty,INPUT_FILTERis applied to all files. FILTER_SOURCE_FILES- If the
FILTER_SOURCE_FILEStag is set toYES, the input filter (if set using INPUT_FILTER ) will also be used to filter the input files that are used for producing the source files to browse (i.e. when SOURCE_BROWSER is set to YES).
Source browsing related options
SOURCE_BROWSER- If the
SOURCE_BROWSERtag is set toYESthen a list of source files will
" be generated. Documented entities will be cross-referenced with these sources.
" Note: To get rid of all source code in the generated output, make sure also
"VERBATIM_HEADERSis set to NO.
" INLINE_SOURCES- Setting the
INLINE_SOURCEStag toYESwill include the body of functions, classes and enums directly into the documentation. STRIP_CODE_COMMENTS- Setting the
STRIP_CODE_COMMENTStag toYES(the default) will instruct doxygen to hide any special comment blocks from generated source code fragments. Normal C and C++ comments will always remain visible. REFERENCED_BY_RELATION- If the
REFERENCED_BY_RELATIONtag is set toYESthen for each documented function all documented functions referencing it will be listed. REFERENCES_RELATION- If the
REFERENCES_RELATIONtag is set toYESthen for each documented function all documented entities called/used by that function will be listed. REFERENCES_LINK_SOURCE- If the
REFERENCES_LINK_SOURCEtag is set toYES(the default) and SOURCE_BROWSER tag is set toYES, then the hyperlinks from functions in REFERENCES_RELATION and REFERENCED_BY_RELATION lists will link to the source code. Otherwise they will link to the documentstion. VERBATIM_HEADERS- If the
VERBATIM_HEADERStag is set theYES(the default) then doxygen will generate a verbatim copy of the header file for each class for which an include is specified. Set to NO to disable this.- See also:
- Section \class.
USE_HTAGS- If the
USE_HTAGStag is set toYESthen the references to source code will point to the HTML generated by the htags(1) tool instead of doxygen built-in source browser. The htags tool is part of GNU's global source tagging system (see http://www.gnu.org/software/global/global.html). The use it do the following:- Install the latest version of global (i.e. 4.8.6 or better)
- Enable SOURCE_BROWSER and USE_HTAGS in the config file
- Make sure the INPUT points to the root of the source tree
- Run doxygen as normal
Doxygen will invoke htags (and that will in turn invoke gtags), so these tools must be available from the command line (i.e. in the search path).
The result: instead of the source browser generated by doxygen, the links to source code will now point to the output of htags.
Alphabetical index options
ALPHABETICAL_INDEX- If the
ALPHABETICAL_INDEXtag is set toYES, an alphabetical index of all compounds will be generated. Enable this if the project contains a lot of classes, structs, unions or interfaces. COLS_IN_ALPHA_INDEX- If the alphabetical index is enabled (see
ALPHABETICAL_INDEX) then theCOLS_IN_ALPHA_INDEXtag can be used to specify the number of columns in which this list will be split (can be a number in the range [1..20]) IGNORE_PREFIX- In case all classes in a project start with a common prefix, all classes will be put under the same header in the alphabetical index. The
IGNORE_PREFIXtag can be used to specify a prefix (or a list of prefixes) that should be ignored while generating the index headers.
HTML related options
GENERATE_HTML- If the
GENERATE_HTMLtag is set toYES(the default) doxygen will generate HTML output HTML_OUTPUT- The
HTML_OUTPUTtag is used to specify where the HTML docs will be put. If a relative path is entered the value ofOUTPUT_DIRECTORYwill be put in front of it. If left blank `html' will be used as the default path. HTML_FILE_EXTENSION- The
HTML_FILE_EXTENSIONtag can be used to specify the file extension for each generated HTML page (for example: .htm, .php, .asp). If it is left blank doxygen will generate files with .html extension. HTML_HEADER- The
HTML_HEADERtag can be used to specify a user-defined HTML header file for each generated HTML page. To get valid HTML the header file should contain at least a<HTML>and a<BODY>tag, but it is good idea to include the style sheet that is generated by doxygen as well. Minimal example:If the tag is left blank doxygen will generate a standard header.<HTML> <HEAD> <TITLE>My title</TITLE> <LINK HREF="doxygen.css" REL="stylesheet" TYPE="text/css"> </HEAD> <BODY BGCOLOR="#FFFFFF">The following commands have a special meaning inside the header:
$title,$datetime,$date,$doxygenversion,$projectname, and$projectnumber. Doxygen will replace them by respectively the title of the page, the current date and time, only the current date, the version number of doxygen, the project name (seePROJECT_NAME), or the project number (seePROJECT_NUMBER).If
CREATE_SUBDIRSis enabled, the command$relpath$can be used to produce a relative path to the root of the HTML output directory, e.g. use $relpath$doxygen.css, to refer to the standard style sheet.See also section Doxygen usage for information on how to generate the default header that doxygen normally uses.
HTML_FOOTER- The
HTML_FOOTERtag can be used to specify a user-defined HTML footer for each generated HTML page. To get valid HTML the footer file should contain at least a</BODY>and a</HTML>tag. A minimal example:If the tag is left blank doxygen will generate a standard footer.</BODY> </HTML>The following commands have a special meaning inside the footer:
$title,$datetime,$date,$doxygenversion,$projectname,$projectnumber. Doxygen will replace them by respectively the title of the page, the current date and time, only the current date, the version number of doxygen, the project name (seePROJECT_NAME), or the project number (seePROJECT_NUMBER).See also section Doxygen usage for information on how to generate the default footer that doxygen normally uses.
HTML_STYLESHEET- The
HTML_STYLESHEETtag can be used to specify a user-defined cascading style sheet that is used by each HTML page. It can be used to fine-tune the look of the HTML output. If the tag is left blank doxygen will generate a default style sheet.See also section Doxygen usage for information on how to generate the style sheet that doxygen normally uses.
HTML_ALIGN_MEMBERS- If the
HTML_ALIGN_MEMBERStag is set toYES, the members of classes, files or namespaces will be aligned in HTML using tables. If set toNOa bullet list will be used.Note: Setting this tag to
NOwill become obsolete in the future, since I only intent to support and test the aligned representation. HTML_DYNAMIC_SECTIONS- If the
HTML_DYNAMIC_SECTIONStag is set toYESthen the generated HTML documentation will contain sections that can be hidden and shown after the page has loaded. For this to work a browser that supports JavaScript and DHTML is required (for instance Mozilla 1.0+, Firefox Netscape 6.0+, Internet explorer 5.0+, Konqueror, or Safari). GENERATE_DOCSET- If the
GENERATE_DOCSETtag is set toYES, additional index files will be generated that can be used as input for Apple's Xcode 3 integrated development environment, introduced with OSX 10.5 (Leopard). To create a documentation set, doxygen will generate a Makefile in the HTML output directory. Runningmakewill produce the docset in that directory and runningmake installwill install the docset in~/Library/Developer/Shared/Documentation/DocSetsso that Xcode will find it at startup. See this article for more information. DOCSET_FEEDNAME- When
GENERATE_DOCSETtag is set toYES, this tag determines the name of the feed. A documentation feed provides an umbrella under which multiple documentation sets from a single provider (such as a company or product suite) can be grouped. DOCSET_BUNDLE_ID- When
GENERATE_DOCSETtag is set toYES, this tag specifies a string that should uniquely identify the documentation set bundle. This should be a reverse domain-name style string, e.g.com.mycompany.MyDocSet. Doxygen will append.docsetto the name. GENERATE_HTMLHELP- If the
GENERATE_HTMLHELPtag is set toYESthen doxygen generates three additional HTML index files:index.hhp,index.hhc, andindex.hhk. Theindex.hhpis a project file that can be read by Microsoft's HTML Help Workshop on Windows.The HTML Help Workshop contains a compiler that can convert all HTML output generated by doxygen into a single compiled HTML file (.chm). Compiled HTML files are now used as the Windows 98 help format, and will replace the old Windows help format (.hlp) on all Windows platforms in the future. Compressed HTML files also contain an index, a table of contents, and you can search for words in the documentation. The HTML workshop also contains a viewer for compressed HTML files.
CHM_FILE- If the
GENERATE_HTMLHELPtag is set toYES, theCHM_FILEtag can be used to specify the file name of the resulting .chm file. You can add a path in front of the file if the result should not be written to the html output directory. HHC_LOCATION- If the
GENERATE_HTMLHELPtag is set toYES, theHHC_LOCATIONtag can be used to specify the location (absolute path including file name) of the HTML help compiler (hhc.exe). If non-empty doxygen will try to run the HTML help compiler on the generated index.hhp. GENERATE_CHI- If the
GENERATE_HTMLHELPtag is set toYES, theGENERATE_CHIflag controls if a separate .chi index file is generated (YES) or that it should be included in the master .chm file (NO). BINARY_TOC- If the
GENERATE_HTMLHELPtag is set toYES, theBINARY_TOCflag controls whether a binary table of contents is generated (YES) or a normal table of contents (NO) in the .chm file. TOC_EXPAND- The
TOC_EXPANDflag can be set to YES to add extra items for group members to the table of contents of the HTML help documentation and to the tree view. GENERATE_QHP- If the GENERATE_QHP tag is set to YES and both QHP_NAMESPACE and QHP_VIRTUAL_FOLDER are set, an additional index file will be generated that can be used as input for Qt's qhelpgenerator to generate a Qt Compressed Help (.qch) of the generated HTML documentation.
QHP_NAMESPACE- The QHP_NAMESPACE tag specifies the namespace to use when generating Qt Help Project output. For more information please see Qt Help Project / Namespace.
QHP_VIRTUAL_FOLDER- The QHP_VIRTUAL_FOLDER tag specifies the namespace to use when generating Qt Help Project output. For more information please see Qt Help Project / Virtual Folders.
QHG_LOCATION- If the GENERATE_QHP tag is set to YES, the QHG_LOCATION tag can be used to specify the location of Qt's qhelpgenerator. If non-empty doxygen will try to run qhelpgenerator on the generated .qhp file.
DISABLE_INDEX- If you want full control over the layout of the generated HTML pages it might be necessary to disable the index and replace it with your own. The
DISABLE_INDEXtag can be used to turn on/off the condensed index at top of each page. A value of NO (the default) enables the index and the value YES disables it. ENUM_VALUES_PER_LINE- This tag can be used to set the number of enum values (range [1..20]) that doxygen will group on one line in the generated HTML documentation.
GENERATE_TREEVIEW- The GENERATE_TREEVIEW tag is used to specify whether a tree-like index structure should be generated to display hierarchical information. If the tag value is set to FRAME, a side panel will be generated containing a tree-like index structure (just like the one that is generated for HTML Help). For this to work a browser that supports JavaScript, DHTML, CSS and frames is required (for instance Mozilla 1.0+, Netscape 6.0+, Internet explorer 5.0+, or Konqueror). Windows users are probably better off using the HTML help feature. Other possible values for this tag are:
HIERARCHIES, which will generate the Groups, Directories, and Class Hierarchy pages using a tree view instead of an ordered list; ALL, which combines the behavior ofFRAMEandHIERARCHIES, andNONE, which disables this behavior completely. For backwards compatibility with previous releases of Doxygen, the values YES and NO are equivalent to FRAME and NONE respectively.Via custom stylesheets (see HTML_STYLESHEET) one can further fine tune the look of the index. As an example, the default style sheet generated by doxygen has an example that shows how to put an image at the root of the tree instead of the project name.
TREEVIEW_WIDTH- If the treeview is enabled (see
GENERATE_TREEVIEW) then this tag can be used to set the initial width (in pixels) of the frame in which the tree is shown. FORMULA_FONTSIZE- Use this tag to change the font size of Latex formulas included as images in the HTML documentation. The default is 10. when you change the font size after a successful doxygen run you need to manually remove any
form_*.pngimages from the HTML output directory to force them to be regenerated.
LaTeX related options
GENERATE_LATEX- If the
GENERATE_LATEXtag is set toYES(the default) doxygen will generate output.
output. LATEX_OUTPUT- The
LATEX_OUTPUTtag is used to specify where the docs will be put. If a relative path is entered the value of
docs will be put. If a relative path is entered the value of OUTPUT_DIRECTORYwill be put in front of it. If left blank `latex' will be used as the default path. LATEX_CMD_NAME- The
LATEX_CMD_NAMEtag can be used to specify the LaTeX command name to be invoked. If left blank `latex' will be used as the default command name. MAKEINDEX_CMD_NAME- The MAKEINDEX_CMD_NAME tag can be used to specify the command name to generate index for LaTeX. If left blank `makeindex' will be used as the default command name.
COMPACT_LATEX- If the
COMPACT_LATEXtag is set toYESdoxygen generates more compact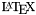 documents. This may be useful for small projects and may help to save some trees in general.
documents. This may be useful for small projects and may help to save some trees in general. PAPER_TYPE- The
PAPER_TYPEtag can be used to set the paper type that is used by the printer. Possible values are:-
a4(210 x 297 mm). -
a4wide(same as a4, but including the a4wide package). -
letter(8.5 x 11 inches). -
legal(8.5 x 14 inches). -
executive(7.25 x 10.5 inches)
-
EXTRA_PACKAGES- The
EXTRA_PACKAGEStag can be used to specify one or more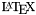 package names that should be included in the
package names that should be included in the 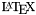 output. To get the times font for instance you can specify If left blank no extra packages will be included.
output. To get the times font for instance you can specify If left blank no extra packages will be included.EXTRA_PACKAGES = times
LATEX_HEADER- The
LATEX_HEADERtag can be used to specify a personal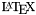 header for the generated
header for the generated  document. The header should contain everything until the first chapter.
document. The header should contain everything until the first chapter.If it is left blank doxygen will generate a standard header. See section Doxygen usage for information on how to let doxygen write the default header to a separate file.
- Note:
- Only use a user-defined header if you know what you are doing!
$title,$datetime,$date,$doxygenversion,$projectname,$projectnumber. Doxygen will replace them by respectively the title of the page, the current date and time, only the current date, the version number of doxygen, the project name (seePROJECT_NAME), or the project number (seePROJECT_NUMBER). PDF_HYPERLINKSIf the
PDF_HYPERLINKStag is set toYES, the that is generated is prepared for conversion to PDF (using ps2pdf or pdflatex). The PDF file will contain links (just like the HTML output) instead of page references. This makes the output suitable for online browsing using a PDF viewer.
that is generated is prepared for conversion to PDF (using ps2pdf or pdflatex). The PDF file will contain links (just like the HTML output) instead of page references. This makes the output suitable for online browsing using a PDF viewer.USE_PDFLATEXIf the
LATEX_PDFLATEXtag is set toYES, doxygen will use pdflatex to generate the PDF file directly from the files.
files.LATEX_BATCHMODEIf the
LATEX_BATCHMODEtag is set toYES, doxygen will add the \batchmode. command to the generated files. This will instruct
files. This will instruct 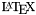 to keep running if errors occur, instead of asking the user for help. This option is also used when generating formulas in HTML.
to keep running if errors occur, instead of asking the user for help. This option is also used when generating formulas in HTML.LATEX_HIDE_INDICESIf
LATEX_HIDE_INDICESis set toYESthen doxygen will not include the index chapters (such as File Index, Compound Index, etc.) in the output.
RTF related options
GENERATE_RTF- If the
GENERATE_RTFtag is set toYESdoxygen will generate RTF output. The RTF output is optimized for Word 97 and may not look too pretty with other readers/editors. RTF_OUTPUT- The
RTF_OUTPUTtag is used to specify where the RTF docs will be put. If a relative path is entered the value ofOUTPUT_DIRECTORYwill be put in front of it. If left blankrtfwill be used as the default path. COMPACT_RTF- If the
COMPACT_RTFtag is set toYESdoxygen generates more compact RTF documents. This may be useful for small projects and may help to save some trees in general. RTF_HYPERLINKS- If the
RTF_HYPERLINKStag is set toYES, the RTF that is generated will contain hyperlink fields. The RTF file will contain links (just like the HTML output) instead of page references. This makes the output suitable for online browsing using Word or some other Word compatible reader that support those fields.- note:
- WordPad (write) and others do not support links.
RTF_STYLESHEET_FILE- Load stylesheet definitions from file. Syntax is similar to doxygen's config file, i.e. a series of assignments. You only have to provide replacements, missing definitions are set to their default value.
See also section Doxygen usage for information on how to generate the default style sheet that doxygen normally uses.
RTF_EXTENSIONS_FILE- Set optional variables used in the generation of an RTF document. Syntax is similar to doxygen's config file. A template extensions file can be generated using
doxygen -e rtf extensionFile.
Man page related options
GENERATE_MAN- If the
GENERATE_MANtag is set toYES(the default) doxygen will generate man pages for classes and files. MAN_OUTPUT- The
MAN_OUTPUTtag is used to specify where the man pages will be put. If a relative path is entered the value ofOUTPUT_DIRECTORYwill be put in front of it. If left blank `man' will be used as the default path. A directory man3 will be created inside the directory specified byMAN_OUTPUT. MAN_EXTENSION- The
MAN_EXTENSIONtag determines the extension that is added to the generated man pages (default is the subroutine's section .3) MAN_LINKS- If the
MAN_LINKStag is set toYESand doxygen generates man output, then it will generate one additional man file for each entity documented in the real man page(s). These additional files only source the real man page, but without them the man command would be unable to find the correct page. The default isNO.
XML related options
GENERATE_XML- If the
GENERATE_XMLtag is set toYESDoxygen will generate an XML file that captures the structure of the code including all documentation. XML_OUTPUT- The
XML_OUTPUTtag is used to specify where the XML pages will be put. If a relative path is entered the value ofOUTPUT_DIRECTORYwill be put in front of it. If left blankxmlwill be used as the default path. XML_SCHEMA- The
XML_SCHEMAtag can be used to specify an XML schema, which can be used by a validating XML parser to check the syntax of the XML files. XML_DTD- The
XML_DTDtag can be used to specify an XML DTD, which can be used by a validating XML parser to check the syntax of the XML files. XML_PROGRAMLISTING- If the
XML_PROGRAMLISTINGtag is set toYESDoxygen will dump the program listings (including syntax highlighting and cross-referencing information) to the XML output. Note that enabling this will significantly increase the size of the XML output.
AUTOGEN_DEF related options
GENERATE_AUTOGEN_DEF- If the
GENERATE_AUTOGEN_DEFtag is set toYESDoxygen will generate an AutoGen Definitions (see http://autogen.sf.net) file that captures the structure of the code including all documentation. Note that this feature is still experimental and incomplete at the moment.
PERLMOD related options
GENERATE_PERLMOD- If the
GENERATE_PERLMODtag is set toYESDoxygen will generate a Perl module file that captures the structure of the code including all documentation. Note that this feature is still experimental and incomplete at the moment. PERLMOD_LATEX- If the
PERLMOD_LATEXtag is set toYESDoxygen will generate the necessary Makefile rules, Perl scripts and LaTeX code to be able to generate PDF and DVI output from the Perl module output. PERLMOD_PRETTY- If the
PERLMOD_PRETTYtag is set toYESthe Perl module output will be nicely formatted so it can be parsed by a human reader. This is useful if you want to understand what is going on. On the other hand, if this tag is set toNOthe size of the Perl module output will be much smaller and Perl will parse it just the same. PERLMOD_MAKEVAR_PREFIX- The names of the make variables in the generated doxyrules.make file are prefixed with the string contained in
PERLMOD_MAKEVAR_PREFIX. This is useful so different doxyrules.make files included by the same Makefile don't overwrite each other's variables.
Preprocessor related options
ENABLE_PREPROCESSING- If the
ENABLE_PREPROCESSINGtag is set toYES(the default) doxygen will evaluate all C-preprocessor directives found in the sources and include files. MACRO_EXPANSION- If the
MACRO_EXPANSIONtag is set toYESdoxygen will expand all macro names in the source code. If set toNO(the default) only conditional compilation will be performed. Macro expansion can be done in a controlled way by settingEXPAND_ONLY_PREDEFtoYES. EXPAND_ONLY_PREDEF- If the
EXPAND_ONLY_PREDEFandMACRO_EXPANSIONtags are both set to YES then the macro expansion is limited to the macros specified with thePREDEFINEDandEXPAND_AS_DEFINEDtags. SEARCH_INCLUDES- If the
SEARCH_INCLUDEStag is set toYES(the default) the includes files in theINCLUDE_PATH(see below) will be searched if a #include is found. INCLUDE_PATH- The
INCLUDE_PATHtag can be used to specify one or more directories that contain include files that are not input files but should be processed by the preprocessor. PREDEFINED- The
PREDEFINEDtag can be used to specify one or more macro names that are defined before the preprocessor is started (similar to the -D option of gcc). The argument of the tag is a list of macros of the form:nameorname=definition(no spaces). If the definition and the "=" are omitted, "=1" is assumed. To prevent a macro definition from being undefined via #undef or recursively expanded use the := operator instead of the = operator. EXPAND_AS_DEFINED- If the
MACRO_EXPANSIONandEXPAND_ONLY_PREDEFtags are set toYESthen this tag can be used to specify a list of macro names that should be expanded. The macro definition that is found in the sources will be used. Use thePREDEFINEDtag if you want to use a different macro definition. SKIP_FUNCTION_MACROS- If the
SKIP_FUNCTION_MACROStag is set toYES(the default) then doxygen's preprocessor will remove all function-like macros that are alone on a line, have an all uppercase name, and do not end with a semicolon. Such function macros are typically used for boiler-plate code, and will confuse the parser if not removed.
External reference options
TAGFILES- The
TAGFILEStag can be used to specify one or more tagfiles.See section Doxytag usage for more information about the usage of tag files.
Optionally an initial location of the external documentation can be added for each tagfile. The format of a tag file without this location is as follows:
TAGFILES = file1 file2 ...
Adding location for the tag files is done as follows:TAGFILES = file1=loc1 "file2 = loc2" ...
whereloc1andloc2can be relative or absolute paths or URLs, If a location is present for each tag, the installdox tool (see section Installdox usage for more information) does not have to be run to correct the links.- Note:
- Each tag file must have a unique name (where the name does not include the path) If a tag file is not located in the directory in which doxygen is run, you must also specify the path to the tagfile here.
GENERATE_TAGFILE- When a file name is specified after
GENERATE_TAGFILE, doxygen will create a tag file that is based on the input files it reads. See section Doxytag usage for more information about the usage of tag files. ALLEXTERNALS- If the
ALLEXTERNALStag is set toYESall external class will be listed in the class index. If set toNOonly the inherited external classes will be listed. EXTERNAL_GROUPS- If the
EXTERNAL_GROUPStag is set toYESall external groups will be listed in the modules index. If set toNO, only the current project's groups will be listed. PERL_PATH- The
PERL_PATHshould be the absolute path and name of the perl script interpreter (i.e. the result of `which perl').
Dot options
CLASS_DIAGRAMS- If the
CLASS_DIAGRAMStag is set toYES(the default) doxygen will generate a class diagram (in HTML and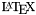 ) for classes with base or super classes. Setting the tag to
) for classes with base or super classes. Setting the tag to NOturns the diagrams off. Note that this option is superseded by the HAVE_DOT option below. This is only a fallback. It is recommended to install and use dot, since it yields more powerful graphs. MSCGEN_PATH- You can define message sequence charts within doxygen comments using the \msc command. Doxygen will then run the msgen tool) to produce the chart and insert it in the documentation. The
MSCGEN_PATHtag allows you to specify the directory where the mscgen tool resides. If left empty the tool is assumed to be found in the default search path. HAVE_DOT- If you set the
HAVE_DOTtag toYESthen doxygen will assume the dot tool is available from the path. This tool is part of Graphviz, a graph visualization toolkit from AT&T and Lucent Bell Labs. The other options in this section have no effect if this option is set toNO(the default) DOT_FONTNAME- By default doxygen will write a font called
FreeSans.ttfto the output directory and reference it in all dot files that doxygen generates. This font does not include all possible unicode characters however, so when you need these (or just want a differently looking font) you can specify the font name usingDOT_FONTNAME. You need need to make sure dot is able to find the font, which can be done by putting it in a standard location or by setting theDOTFONTPATHenvironment variable or by settingDOT_FONTPATHto the directory containing the font. DOT_FONTSIZE- The
DOT_FONTSIZEtag can be used to set the size of the font of dot graphs. The default size is 10pt. DOT_FONTPATH- By default doxygen will tell dot to use the output directory to look for the
FreeSans.ttffont (which doxygen will put there itself). If you specify a different font usingDOT_FONTNAMEyou can set the path where dot can find it using this tag. DOT_FONTNAME- By default doxygen will write a font called FreeSans.ttf to the output directory and reference it in all dot files that doxygen generates. This font does not include all possible unicode characters however, so when you need these (or just want a differently looking font) you can specify the font name using
DOT_FONTNAME. You need need to make sure dot is able to find the font, which can be done by putting it in a standard location or by setting theDOTFONTPATHenvironment variable or by settingDOT_FONTPATHto the directory containing the font. DOT_FONTPATH- By default doxygen will tell dot to use the output directory to look for the FreeSans.ttf font (which doxygen will put there itself). If you specify a different font using
DOT_FONTNAMEyou can set the path where dot can find it using this tag. CLASS_GRAPH- If the
CLASS_GRAPHandHAVE_DOTtags are set toYESthen doxygen will generate a graph for each documented class showing the direct and indirect inheritance relations. Setting this tag toYESwill force the theCLASS_DIAGRAMStag to NO. COLLABORATION_GRAPH- If the
COLLABORATION_GRAPHandHAVE_DOTtags are set toYESthen doxygen will generate a graph for each documented class showing the direct and indirect implementation dependencies (inheritance, containment, and class references variables) of the class with other documented classes. GROUP_GRAPHS- If the GROUP_GRAPHS and HAVE_DOT tags are set to YES then doxygen will generate a graph for groups, showing the direct groups dependencies.
UML_LOOK- If the UML_LOOK tag is set to YES doxygen will generate inheritance and collaboration diagrams in a style similar to the OMG's Unified Modeling Language.
TEMPLATE_RELATIONS- If the
TEMPLATE_RELATIONSandHAVE_DOTtags are set toYESthen doxygen will show the relations between templates and their instances. HIDE_UNDOC_RELATIONS- If set to YES, the inheritance and collaboration graphs will hide inheritance and usage relations if the target is undocumented or is not a class.
INCLUDE_GRAPH- If the
ENABLE_PREPROCESSING,SEARCH_INCLUDES,INCLUDE_GRAPH, andHAVE_DOTtags are set toYESthen doxygen will generate a graph for each documented file showing the direct and indirect include dependencies of the file with other documented files. INCLUDED_BY_GRAPH- If the
ENABLE_PREPROCESSING,SEARCH_INCLUDES,INCLUDED_BY_GRAPH, andHAVE_DOTtags are set toYESthen doxygen will generate a graph for each documented header file showing the documented files that directly or indirectly include this file. CALL_GRAPH- If the
CALL_GRAPHandHAVE_DOTtags are set toYESthen doxygen will generate a call dependency graph for every global function or class method. Note that enabling this option will significantly increase the time of a run. So in most cases it will be better to enable call graphs for selected functions only using the \callgraph command. CALLER_GRAPH- If the
CALLER_GRAPHandHAVE_DOTtags are set toYESthen doxygen will generate a caller dependency graph for every global function or class method. Note that enabling this option will significantly increase the time of a run. So in most cases it will be better to enable caller graphs for selected functions only using the \callergraph command. GRAPHICAL_HIERARCHY- If the
GRAPHICAL_HIERARCHYandHAVE_DOTtags are set toYESthen doxygen will graphical hierarchy of all classes instead of a textual one. DIRECTORY_GRAPH- If the
DIRECTORY_GRAPH,SHOW_DIRECTORIESandHAVE_DOToptions are set toYESthen doxygen will show the dependencies a directory has on other directories in a graphical way. The dependency relations are determined by the #include relations between the files in the directories. DOT_GRAPH_MAX_NODES- The
DOT_GRAPH_MAX_NODEStag can be used to set the maximum number of nodes that will be shown in the graph. If the number of nodes in a graph becomes larger than this value, doxygen will truncate the graph, which is visualized by representing a node as a red box. Note that doxygen if the number of direct children of the root node in a graph is already larger thanDOT_GRAPH_MAX_NODESthen the graph will not be shown at all. Also note that the size of a graph can be further restricted byMAX_DOT_GRAPH_DEPTH. MAX_DOT_GRAPH_DEPTH- The
MAX_DOT_GRAPH_DEPTHtag can be used to set the maximum depth of the graphs generated by dot. A depth value of 3 means that only nodes reachable from the root by following a path via at most 3 edges will be shown. Nodes that lay further from the root node will be omitted. Note that setting this option to 1 or 2 may greatly reduce the computation time needed for large code bases. Also note that the size of a graph can be further restricted byDOT_GRAPH_MAX_NODES. Using a depth of 0 means no depth restriction (the default). DOT_IMAGE_FORMAT- The
DOT_IMAGE_FORMATtag can be used to set the image format of the images generated by dot. Possible values are gif, jpg, and png. If left blank png will be used. DOT_PATH- This tag can be used to specify the path where the dot tool can be found. If left blank, it is assumed the dot tool can be found on the path.
DOTFILE_DIRS- This tag can be used to specify one or more directories that contain dot files that are included in the documentation (see the \dotfile command).
DOT_TRANSPARENT- Set the
DOT_TRANSPARENTtag toYESto generate images with a transparent background. This is disabled by default, because dot on Windows does not seem to support this out of the box. Warning: Depending on the platform used, enabling this option may lead to badly anti-aliased labels on the edges of a graph (i.e. they become hard to read). DOT_MULTI_TARGETS- Set the
DOT_MULTI_TARGETStag toYESallow dot to generate multiple output files in one run (i.e. multiple -o and -T options on the command line). This makes dot run faster, but since only newer versions of dot (>1.8.10) support this, this feature is disabled by default. GENERATE_LEGEND- If the
GENERATE_LEGENDtag is set toYES(the default) doxygen will generate a legend page explaining the meaning of the various boxes and arrows in the dot generated graphs. DOT_CLEANUP- If the
DOT_CLEANUPtag is set toYES(the default) doxygen will remove the intermediate dot files that are used to generate the various graphs.
Search engine options
SEARCHENGINE- The
SEARCHENGINEtag specifies whether or not the HTML output should contain a search facility. Possible values areYESandNO. If set to YES, doxygen will produce a search index and a PHP script to search through the index. For this to work the documentation should be viewed via a web-server running PHP version 4.1.0 or higher. (See http://www.php.net/manual/en/installation.php for installation instructions).
Examples
Suppose you have a simple project consisting of two files: a source file example.cc and a header file example.h. Then a minimal configuration file is as simple as:
INPUT = example.cc example.h
Assuming the example makes use of Qt classes and perl is located in /usr/bin, a more realistic configuration file would be:
PROJECT_NAME = Example INPUT = example.cc example.h WARNINGS = YES TAGFILES = qt.tag PERL_PATH = /usr/bin/perl SEARCHENGINE = NO
To generate the documentation for the QdbtTabular package I have used the following configuration file:
PROJECT_NAME = QdbtTabular OUTPUT_DIRECTORY = html WARNINGS = YES INPUT = examples/examples.doc src FILE_PATTERNS = *.cc *.h INCLUDE_PATH = examples TAGFILES = qt.tag PERL_PATH = /usr/local/bin/perl SEARCHENGINE = YES
To regenerate the Qt-1.44 documentation from the sources, you could use the following config file:
PROJECT_NAME = Qt
OUTPUT_DIRECTORY = qt_docs
HIDE_UNDOC_MEMBERS = YES
HIDE_UNDOC_CLASSES = YES
ENABLE_PREPROCESSING = YES
MACRO_EXPANSION = YES
EXPAND_ONLY_PREDEF = YES
SEARCH_INCLUDES = YES
FULL_PATH_NAMES = YES
STRIP_FROM_PATH = $(QTDIR)/
PREDEFINED = USE_TEMPLATECLASS Q_EXPORT= \
QArrayT:=QArray \
QListT:=QList \
QDictT:=QDict \
QQueueT:=QQueue \
QVectorT:=QVector \
QPtrDictT:=QPtrDict \
QIntDictT:=QIntDict \
QStackT:=QStack \
QDictIteratorT:=QDictIterator \
QListIteratorT:=QListIterator \
QCacheT:=QCache \
QCacheIteratorT:=QCacheIterator \
QIntCacheT:=QIntCache \
QIntCacheIteratorT:=QIntCacheIterator \
QIntDictIteratorT:=QIntDictIterator \
QPtrDictIteratorT:=QPtrDictIterator
INPUT = $(QTDIR)/doc \
$(QTDIR)/src/widgets \
$(QTDIR)/src/kernel \
$(QTDIR)/src/dialogs \
$(QTDIR)/src/tools
FILE_PATTERNS = *.cpp *.h q*.doc
INCLUDE_PATH = $(QTDIR)/include
RECURSIVE = YES
For the Qt-2.1 sources I recommend to use the following settings:
PROJECT_NAME = Qt
PROJECT_NUMBER = 2.1
HIDE_UNDOC_MEMBERS = YES
HIDE_UNDOC_CLASSES = YES
SOURCE_BROWSER = YES
INPUT = $(QTDIR)/src
FILE_PATTERNS = *.cpp *.h q*.doc
RECURSIVE = YES
EXCLUDE_PATTERNS = *codec.cpp moc_* */compat/* */3rdparty/*
ALPHABETICAL_INDEX = YES
COLS_IN_ALPHA_INDEX = 3
IGNORE_PREFIX = Q
ENABLE_PREPROCESSING = YES
MACRO_EXPANSION = YES
INCLUDE_PATH = $(QTDIR)/include
PREDEFINED = Q_PROPERTY(x)= \
Q_OVERRIDE(x)= \
Q_EXPORT= \
Q_ENUMS(x)= \
"QT_STATIC_CONST=static const " \
_WS_X11_ \
INCLUDE_MENUITEM_DEF
EXPAND_ONLY_PREDEF = YES
EXPAND_AS_DEFINED = Q_OBJECT_FAKE Q_OBJECT ACTIVATE_SIGNAL_WITH_PARAM \
Q_VARIANT_AS
Here doxygen's preprocessor is used to substitute some macro names that are normally substituted by the C preprocessor, but without doing full macro expansion.
 1.5.7.1
1.5.7.1