Automatic link generation
Most documentation systems have special `see also' sections where links to other pieces of documentation can be inserted. Although doxygen also has a command to start such a section (See section \sa), it does allow you to put these kind of links anywhere in the documentation. For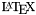 documentation a reference to the page number is written instead of a link. Furthermore, the index at the end of the document can be used to quickly find the documentation of a member, class, namespace or file. For man pages no reference information is generated.
documentation a reference to the page number is written instead of a link. Furthermore, the index at the end of the document can be used to quickly find the documentation of a member, class, namespace or file. For man pages no reference information is generated.The next sections show how to generate links to the various documented entities in a source file.
Links to web pages and mail addresses
Doxygen will automatically replace any URLs and mail addresses found in the documentation by links (in HTML).Links to classes.
All words in the documentation that correspond to a documented class and contain at least one upper case character will automatically be replaced by a link to the page containing the documentation of the class. If you want to prevent that a word that corresponds to a documented class is replaced by a link you should put a % in front of the word.Links to files.
All words that contain a dot (.) that is not the last character in the word are considered to be file names. If the word is indeed the name of a documented input file, a link will automatically be created to the documentation of that file.Links to functions.
Links to functions are created if one of the following patterns is encountered:-
<functionName>"("<argument-list>")" -
<functionName>"()" -
"::"<functionName> -
(<className>"::")n<functionName>"("<argument-list>")" -
(<className>"::")n<functionName>"("<argument-list>")"<modifiers> -
(<className>"::")n<functionName>"()" -
(<className>"::")n<functionName>
- Note 1:
- Function arguments should be specified with correct types, i.e. 'fun(const std::string&,bool)' or '()' to match any prototype.
- Note 2:
- Member function modifiers (like 'const' and 'volatile') are required to identify the target, i.e. 'func(int) const' and 'fun(int)' target different member functions.
- Note 3:
- For JavaDoc compatibility a # may be used instead of a :: in the patterns above.
- Note 4:
- In the documentation of a class containing a member foo, a reference to a global variable is made using foo, whereas #foo will link to the member.
If a function is overloaded and no matching argument list is specified (i.e. pattern 2 or 6 is used), a link will be created to the documentation of one of the overloaded members.
For member functions the class scope (as used in patterns 4 to 7) may be omitted, if:
- The pattern points to a documented member that belongs to the same class as the documentation block that contains the pattern.
- The class that corresponds to the documentation blocks that contains the pattern has a base class that contains a documented member that matches the pattern.
Links to variables, typedefs, enum types, enum values and defines.
All of these entities can be linked to in the same way as described in the previous section. For sake of clarity it is advised to only use patterns 3 and 7 in this case.
- Example:
- Click here for the corresponding HTML documentation that is generated by Doxygen.
/*! \file autolink.cpp Testing automatic link generation. A link to a member of the Test class: Test::member, More specific links to the each of the overloaded members: Test::member(int) and Test#member(int,int) A link to a protected member variable of Test: Test#var, A link to the global enumeration type #GlobEnum. A link to the define #ABS(x). A link to the destructor of the Test class: Test::~Test, A link to the typedef ::B. A link to the enumeration type Test::EType A link to some enumeration values Test::Val1 and ::GVal2 */ /*! Since this documentation block belongs to the class Test no link to Test is generated. Two ways to link to a constructor are: #Test and Test(). Links to the destructor are: #~Test and ~Test(). A link to a member in this class: member(). More specific links to the each of the overloaded members: member(int) and member(int,int). A link to the variable #var. A link to the global typedef ::B. A link to the global enumeration type #GlobEnum. A link to the define ABS(x). A link to a variable \link #var using another text\endlink as a link. A link to the enumeration type #EType. A link to some enumeration values: \link Test::Val1 Val1 \endlink and ::GVal1. And last but not least a link to a file: autolink.cpp. \sa Inside a see also section any word is checked, so EType, Val1, GVal1, ~Test and member will be replaced by links in HTML. */ class Test { public: Test(); //!< constructor ~Test(); //!< destructor void member(int); /**< A member function. Details. */ void member(int,int); /**< An overloaded member function. Details */ /** An enum type. More details */ enum EType { Val1, /**< enum value 1 */ Val2 /**< enum value 2 */ }; protected: int var; /**< A member variable */ }; /*! details. */ Test::Test() { } /*! details. */ Test::~Test() { } /*! A global variable. */ int globVar; /*! A global enum. */ enum GlobEnum { GVal1, /*!< global enum value 1 */ GVal2 /*!< global enum value 2 */ }; /*! * A macro definition. */ #define ABS(x) (((x)>0)?(x):-(x)) typedef Test B; /*! \fn typedef Test B * A type definition. */
typedefs.
Typedefs that involve classes, structs and unions, liketypedef struct StructName TypeName
- Example:
- Click here for the corresponding HTML documentation that is generated by Doxygen.
/*! \file restypedef.cpp * An example of resolving typedefs. */ /*! \struct CoordStruct * A coordinate pair. */ struct CoordStruct { /*! The x coordinate */ float x; /*! The y coordinate */ float y; }; /*! Creates a type name for CoordStruct */ typedef CoordStruct Coord; /*! * This function returns the addition of \a c1 and \a c2, i.e: * (c1.x+c2.x,c1.y+c2.y) */ Coord add(Coord c1,Coord c2) { }
 1.5.7.1
1.5.7.1